Picks of our best science in 2021
December 2021: Juan Amaro-Gahete, Mariia V. Pavliuk, Haining Tian, Dolores Esquivel, Francisco J. Romero-Salguero, and Sascha Ott published a review article in Coordination Chemistry Reviews:
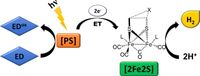
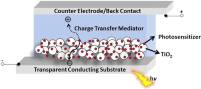
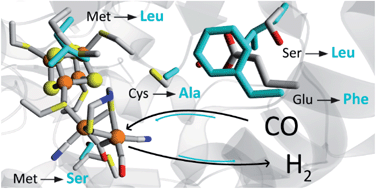
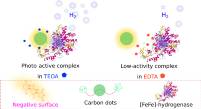
Abstract: A global hydrogen economy could ensure environmentally sustainable, safe and cost-efficient renewable energy for the 21st century. Solar hydrogen production through artificial photosynthesis is a key strategy, and the activity of natural hydrogenase metalloenzymes an inspiration for the design of synthetic catalyst systems. Herein, we take an extensive journey through the field of biomimetic hydrogenase chemistry for light-driven hydrogen production. We open with a brief presentation of the structure and redox mechanism of the natural enzyme. Synthetic methodologies, structural characteristics, and hydrogen generation metrics relevant to the synthetic diiron catalysts ([2Fe2S]) are discussed. This review illuminates the most useful aspects to rationally design a wide variety of biomimetic catalysts inspired by the diiron subsite of [FeFe]-hydrogenases, and establishes design features shared by the most stable and efficient hydrogen producing photosystems.
December 2021: Xinjian Geng, Mohamed Abdellah, Robert Bericat Vadell, Matilda Folkenant,Tomas Edvinsson and Jacinto Sá published an article in Nanomaterials:
Direct Plasmonic Solar Cell Efficiency Dependence on Spiro-OMeTAD Li-TFSI Content.
Abstract: The proliferation of the internet of things (IoT) and other low-power devices demands the development of energy harvesting solutions to alleviate IoT hardware dependence on single-use batteries, making their deployment more sustainable. The propagation of energy harvesting solutions is strongly associated with technical performance, cost and aesthetics, with the latter often being the driver of adoption. The general abundance of light in the vicinity of IoT devices under their main operation window enables the use of indoor and outdoor photovoltaics as energy harvesters. From those, highly transparent solar cells allow an increased possibility to place a sustainable power source close to the sensors without significant visual appearance. Herein, we report the effect of hole transport layer Li-TFSI dopant content on semi-transparent, direct plasmonic solar cells (DPSC) with a transparency of more than 80% in the 450–800 nm region. The results show that the system can be made highly transparent by precise tuning of the doping level of the spiro-OMeTAD layer with retained plasmonics, large optical cross-sections and the ultrathin nature of the devices.
October 2021: Joakim Ekspong, Christian Larsen, Jonas Stenberg, Wai Ling Kwong, Jia Wang, Jinbao Zhang, Erik M. J. Johansson, Johannes Messinger, Ludvig Edman, and Thomas Wågberg published an article in ACS Sustainable Chemistry Engineering:
Abstract: We present the synthesis and characterization of an efficient and low cost solar-driven electrolyzer consisting of Earth-abundant materials. The trimetallic NiFeMo electrocatalyst takes the shape of nanometer-sized flakes anchored to a fully carbon-based current collector comprising a nitrogen-doped carbon nanotube network, which in turn is grown on a carbon fiber paper support. This catalyst electrode contains solely Earth-abundant materials, and the carbon fiber support renders it effective despite a low metal content. Notably, a bifunctional catalyst–electrode pair exhibits a low total overpotential of 450 mV to drive a full water-splitting reaction at a current density of 10 mA cm–2 and a measured hydrogen Faradaic efficiency of ∼100%. We combine the catalyst–electrode pair with solution-processed perovskite solar cells to form a lightweight solar-driven water-splitting device with a high peak solar-to-fuel conversion efficiency of 13.8%.
September 2021: Casper de Lichtenberg, ChristopherJ. Kim, Petko Chernev, Richard J. Debus and Johannes Messinger published an article in Chemical Science:
Abstract: The molecular oxygen we breathe is produced from water-derived oxygen species bound to the Mn4CaO5 cluster in photosystem II (PSII). Present research points to the central oxo-bridge O5 as the ‘slow exchanging substrate water (Ws)’, while, in the S2 state, the terminal water ligands W2 and W3 are both discussed as the ‘fast exchanging substrate water (Wf)’. A critical point for the assignment of Wf is whether or not its exchange with bulk water is limited by barriers in the channels leading to the Mn4CaO5 cluster. In this study, we measured the rates of substrate water exchange in the S2 and S3 states of PSII core complexes from wild-type (WT) Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803, and from two mutants, D1-D61A and D1-E189Q, that are expected to alter water access via the Cl1/O4 channels and the O1 channel, respectively. We found that the exchange rates of Wf and Ws were unaffected by the E189Q mutation (O1 channel), but strongly perturbed by the D61A mutation (Cl1/O4 channel). It is concluded that all channels have restrictions limiting the isotopic equilibration of the inner water pool near the Mn4CaO5 cluster, and that D61 participates in one such barrier.
August 2021: Wailing Kwong, Thomas Wågberg, and Johannes Messinger published an article in International Journal of Hydrogen Energy:
Abstract: Ammonia production via the electrochemical N2 reduction reaction (NRR) at ambient conditions is highly desired as an alternative to the Haber-Bosch process, but remains a great challenge due to the low efficiency and selectivity caused by the competing hydrogen evolution reaction (HER). Herein we investigate the effect of availabilities of reactants (protons, electrons and N2) on NRR using a FeOx-coated carbon fiber paper cathode in various electrochemical configurations. NRR is found viable only under the conditions of low proton- and high N2 availabilities, which are achieved using 0.12 vol% water in LiClO4-ethyl acetate electrolyte and gaseous N2 supplied to the membrane-electrode assembly cathode. Other conditions (high proton-, or low N2-availability, or both) yield a lower or negligible amount of ammonia due to the competing HER. Our work shows that promoting NRR by suppressing the HER requires optimization of the operational variables, which serves as a complementary strategy to the development of NRR catalysts.
August 2021: Robin N. Dürr, Pierfrancesco Maltoni, Haining Tian, Bruno Jousselme, Leif Hammarström, and Tomas Edvinsson published an article in ACS Nano:
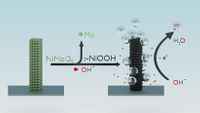
Abstract: Water electrolysis powered by renewable energies is a promising technology to produce sustainable fossil free fuels. The development and evaluation of effective catalysts are here imperative; however, due to the inclusion of elements with different redox properties and reactivity, these materials undergo dynamical changes and phase transformations during the reaction conditions. NiMoO4 is currently investigated among other metal oxides as a promising noble metal free catalyst for the oxygen evolution reaction. Here we show that at applied bias, NiMoO4·H2O transforms into γ-NiOOH. Time resolved operando Raman spectroscopy is utilized to follow the potential dependent phase transformation and is collaborated with elemental analysis of the electrolyte, confirming that molybdenum leaches out from the as-synthesized NiMoO4·H2O. Molybdenum leaching increases the surface coverage of exposed nickel sites, and this in combination with the formation of γ-NiOOH enlarges the amount of active sites of the catalyst, leading to high current densities. Additionally, we discovered different NiMoO4 nanostructures, nanoflowers, and nanorods, for which the relative ratio can be influenced by the heating ramp during the synthesis.
July 2021: Nora Eliasson, Belinda Pettersson Rimgard, Ashleigh Castner, Cheuk-Wai Tai, Sascha Ott, Haining Tian, and Leif Hammarström published an article in Journal of Physical Chemistry C:
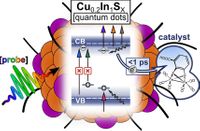
Abstract: The photophysical properties of Cu-deficient Cu0.2In1Sx quantum dots synthesized through a facile aqueous-based procedure have been investigated. Transient absorption experiments were carried out probing in the UV–vis, near-IR, and mid-IR regions, with the aim to (i) study the photophysical properties of the quantum dots and (ii) monitor kinetics of electron transfer to a molecular catalyst.
A model complex of the [Fe2]-hydrogenase active site was introduced to explore the potential of the quantum dots as photosensitizers for molecular catalysts. The quantum dot photoluminescence was quenched upon catalyst addition, and direct evidence of the singly reduced catalyst was found by transient absorption in the UV–vis and mid-IR. The catalyst accepted reducing equivalents on a subpicosecond time scale upon photoexcitation of the quantum dots, despite no covalent linking chemistry being applied. This implies that charge transfer is not limited by diffusion rates, thus confirming the presence of spontaneous quantum dot and catalyst self-assembly.
June 2021: João S. Rodrigues and Pia Lindberg published an article in Metabolic Engineering Communications:
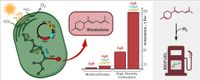
Metabolic engineering of Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803 for improved bisabolene production.
Abstract: Terpenoids are a wide class of organic compounds with industrial relevance. The natural ability of cyanobacteria to produce terpenoids via the methylerythritol 4-phosphate (MEP) pathway makes these organisms appealing candidates for the generation of light-driven cell factories for green chemistry. Here we address the improvement of the production of (E)-α-bisabolene, a valuable biofuel feedstock, in Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803 via sequential heterologous expression of bottleneck enzymes of the native pathway. Expression of the bisabolene synthase is sufficient to complete the biosynthetic pathway of bisabolene. Expression of a farnesyl-pyrophosphate synthase from Escherichia coli did not influence production of bisabolene, while enhancement of the MEP pathway via additional overexpression of 1-deoxy-D-xylulose-5-phosphate synthase (DXS) and IPP/DMAPP isomerase (IDI) significantly increased production per cell. However, in the absence of a carbon sink, the overexpression of DXS and IDI leads to significant growth impairment. The final engineered strain reached a volumetric titre of 9 mg L−1 culture of bisabolene after growing for 12 days. We conclude that fine-tuning of the cyanobacterial terpenoid pathway is crucial for the generation of microbial platforms for terpenoid production on industrial-scale. |
April 2021: Maxime Laurans, Jordann A. L. Wells, and Sascha Ott published an article in Dalton Transactions:
Abstract: Photoelectrochemical CO2 reduction is a promising approach for renewable fuel generation and to reduce greenhouse gas emissions. Owing to their synthetic tunability, molecular catalysts for the CO2 reduction reaction can give rise to high product selectivity. In this context, a Ru(II) complex was immobilised on a thin SiOx layer of a p-Si electrode that was decorated with a bromide-terminated molecular layer. Following the characterisation of the assembled photocathodes by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy and ellipsometry, PEC experiments demonstrate electron transfer from the p-Si to the Ru complex through the native oxide layer under illumination and a cathodic bias. A state-of-the-art photovoltage of 570 mV was determined by comparison with an analogous n-type Si assembly. While the photovoltage of the modified photocathode is promising for future photoelectrochemical CO2 reduction and the p-Si/SiOx junction seems to be unchanged during the PEC experiments, a fast desorption of the molecular Ru complex was observed. An in-depth investigation of the cathode degradation by comparison with reference materials highlights the role of the hydroxyl functionality of the Ru complex to ensure its grafting on the substrate.
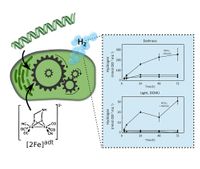
March 2021: Adam Wegelius, Henrik Land, Gustav Berggren, and Peter Lindblad published an article in Cell reports physical science:
Abstract: Hydrogen (H2) is a promising future chemical energy carrier and feedstock with several renewable production options, including electrolyzers and biological/bioinspired systems. The top H2 producers in nature are [FeFe]-hydrogenases, high turnover metalloenzymes with a complex maturation process that can be circumvented by artificial synthetic activation. Here, we report the expression and activation of group A and D [FeFe]-hydrogenases in a photosynthetic host organism, the unicellular cyanobacterium Synechocystis PCC 6803. The hydrogenase from Solobacterium moorei (group A) facilitates high in vivo H2 production from purely photoautotrophically generated substrates and unmistakably links to the metabolism of the photosynthetic host. Cells harboring the non-native, semisynthetic enzyme retain their H2 production capacity for several days after synthetic activation. This work expands both the number and the diversity of [FeFe]-hydrogenases examined in a photosynthetic background and provides important insights for future investigations into the development and understanding of biological and biohybrid H2 production systems.
January 2021: Gerrit Boschloo, Marina Freitag, Leif Hammarström, Erik M J Johansson, Jacinto Sá , Haining Tian, published a feature article in Nanotechnology:
Dye sensitized solar cells In: Nanotechnology for catalysis and solar energy conversion
...and some more from 2020!
December 2020: Henrik Land, Alina Sekretareva, Ping Huang, Holly J. Redman, Brigitta Németh, Nakia Polidori, Lívia S. Mészáros, Moritz Senger, Sven T. Stripp and Gustav Berggren published an article in Chemical Science:
Characterization of a putative sensory [FeFe]-hydrogenase provides new insight into the role of the active site architecture
Abstract: [FeFe]-hydrogenases are known for their high rates of hydrogen turnover, and are intensively studied in the context of biotechnological applications. Evolution has generated a plethora of different subclasses with widely different characteristics. The M2e subclass is phylogenetically distinct from previously characterized members of this enzyme family and its biological role is unknown. It features significant differences in domain- and active site architecture, and is most closely related to the putative sensory [FeFe]-hydrogenases. Here we report the first comprehensive biochemical and spectroscopical characterization of an M2e enzyme, derived from Thermoanaerobacter mathranii. As compared to other [FeFe]-hydrogenases characterized to-date, this enzyme displays an increased H2 affinity, higher activation enthalpies for H+/H2 interconversion, and unusual reactivity towards known hydrogenase inhibitors. These properties are related to differences in active site architecture between the M2e [FeFe]-hydrogenase and “prototypical” [FeFe]-hydrogenases. Thus, this study provides new insight into the role of this subclass in hydrogen metabolism and the influence of the active site pocket on the chemistry of the H-cluster.
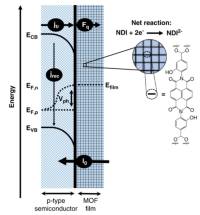
November 2020: Anna M. Beiler , Brian D. McCarthy , Ben A. Johnson and Sascha Ott published an article in Nature communications:
Abstract: Surface modification of semiconductors can improve photoelectrochemical performance by promoting efficient interfacial charge transfer. We show that metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) are viable surface coatings for enhancing cathodic photovoltages. Under 1-sun illumination, no photovoltage is observed for p-type Si(111) functionalized with a naphthalene diimide derivative until the monolayer is expanded in three dimensions in a MOF. The surface-grown MOF thin film at Si promotes reduction of the molecular linkers at formal potentials >300 mV positive of their thermodynamic potentials. The photocurrent is governed by charge diffusion through the film, and the MOF film is sufficiently conductive to power reductive transformations. When grown on GaP(100), the reductions of the MOF linkers are shifted anodically by >700 mV compared to those of the same MOF on conductive substrates.
This photovoltage, among the highest reported for GaP in photoelectrochemical applications, illustrates the power of MOF films to enhance photocathodic operation.
November 2020: Sergey Kosourov, Valéria Nagya, Dmitry Shevela, Martina Jokela, Johannes Messinger and Yagut Allahverdiyeva published an article in The Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the USA:
Significance: Photosynthetic H2 production in the green alga Chlamydomonas reinhardtii is catalyzed by O2-sensitive [FeFe]-hydrogenases, which accept electrons from photosynthetically reduced ferredoxin and reduce protons to H2. Since the process occurs downstream of photosystem I, the contribution of photosystem II (PSII) in H2 photoproduction has long been a subject of debate. Indeed, water oxidation by PSII results in O2 accumulation in chloroplasts, which inhibits H2 evolution. Therefore, clear evidence for direct water biophotolysis resulting in simultaneous H2 and O2 releases in algae has never been presented. This paper demonstrates that sustained H2 photoproduction in C. reinhardtii is directly linked to PSII-dependent water oxidation and brings insights into regulation of PSII activity and H2 production by CO2/HCO3 – under microoxic conditions.
October 2020: Robin Tyburski, Chenyu Wen, Rui Sun, Mohamed Abdellah, Jing Huang, Luca D’Amario, Gerrit Boschloo, Leif Hammarström, and Haining Tian published an article in The Journal of the American Chemical Society:
Understanding the Role of Surface States on Mesoporous NiO Films
Abstract: Surface states of mesoporous NiO semiconductor films have particular properties differing from the bulk and are able to dramatically influence the interfacial electron transfer and adsorption of chemical species. To achieve a better performance of NiO-based p-type dye-sensitized solar cells (p-DSCs), the function of the surface states has to be understood. In this paper, we applied a modified atomic layer deposition procedure that is able to passivate 72% of the surface states on NiO by depositing a monolayer of Al2O3. This provides us with representative control samples to study the functions of the surface states on NiO films. A main conclusion is that surface states, rather than the bulk, are mainly responsible for the conductivity in mesoporous NiO films.
A more complete mechanism is suggested to understand the particular hole transport behavior in p-DSCs, in which the hole transport time is independent of light intensity. This is ascribed to the percolation hole hopping on the surface states. When the concentration of surface states was significantly reduced, the light-independent charge transport behavior in pristine NiO-based p-DSCs transformed into having an exponential dependence on light intensity, similar to that observed in TiO2-based n-type DSCs. These conclusions on the function of surface states provide new insight into the electronic properties of mesoporous NiO films.
June 2020: Astrid Nilsen-Moe, Clorice R. Reinhardt, Starla D. Glover, Li Liang, Sharon Hammes-Schiffer,
Leif Hammarström, and Cecilia Tommos published a paper in Journal of the American Chemical Society:
Proton-Coupled Electron Transfer from Tyrosine in the Interior of a de novo Protein: Mechanisms and Primary Proton Acceptor
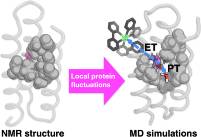
Abstract: Proton-coupled electron transfer (PCET) from tyrosine produces a neutral tyrosyl radical (Y•) that is vital to many catalytic redox reactions. To better understand how the protein environment influences the PCET properties of tyrosine, we have studied the radical formation behavior of Y32 in the α3Y model protein. The previously solved α3Y solution NMR structure shows that Y32 is sequestered ∼7.7 ± 0.3 Å below the protein surface without any primary proton acceptors nearby.
Here we present transient absorption kinetic data and molecular dynamics (MD) simulations to resolve the PCET mechanism associated with Y32 oxidation. Y32• was generated in a bimolecular reaction with [Ru(bpy)3]3+ formed by flash photolysis. At pH > 8, the rate constant of Y32• formation (kPCET) increases by one order of magnitude per pH unit, corresponding to a proton-first mechanism via tyrosinate (PTET). At lower pH < 7.5, the pH dependence is weak and shows a previously measured KIE ≈ 2.5, which best fits a concerted mechanism. MD simulations show that one to two water molecules can enter the hydrophobic cavity of α3Y and hydrogen bond to Y32, as well as the possibility of hydrogen-bonding interactions between Y32 and E13, through structural fluctuations that reorient surrounding side chains. Our results illustrate how protein conformational motions can influence the redox reactivity of a tyrosine residue and how PCET mechanisms can be tuned by changing the pH even when the PCET occurs within the interior of a protein.
June 2020: Kateřina Holá, Mariia V. Pavliuk, Brigitta Németh, Ping Huang, Lukáš Zdražil, Henrik Land, Gustav Berggren, and Haining Tian published an article in ACS Catalysis:
Abstract: Artificial photosynthesis is seen as a path to convert and store solar energy into chemical energy for our society. In this work, highly fluorescent aspartic acid-based carbon dots (CDs) are synthesized and employed as a photosensitizer to drive photocatalytic hydrogen evolution with an [FeFe] hydrogenase (CrHydA1). The study discloses the significant influence of the electrostatic surrounding generated by sacrificial electron donors on the intimate interplay within the oppositely charged subunits of the biohybrid assembly as well as the overall photocatalytic performance. The system reaches an external quantum efficiency of 1.7% at 420 nm and an initial activity of 1.73 μmol(H2) /mg (hydrogenase) /min under favorable electrostatic conditions. Owing to the ability of the synthesized AspCDs to operate efficiently under visible light, in contrast to other materials that require UV illumination, the stability of the biohybrid assembly in the presence of a redox mediator extends beyond 1 week.
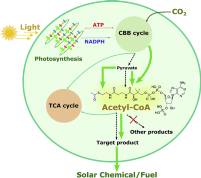
June 2020: Rui Miao, Hao Xie, Xufeng Liu, Pia Lindberg and Peter Lindblad published an article in Current Opinion in Chemical Biology:
Abstract: The production of fuels and other valuable chemicals via biological routes has gained significant attention during last decades. Cyanobacteria are prokaryotes that convert solar energy to chemical compounds in vivo in direct processes. Intensive studies have been carried out with the aim of engineering cyanobacteria as microfactories for solar fuel and chemical production. Engineered strains of photosynthetic cyanobacteria can produce different compounds on a proof-of-concept level, but few products show titers comparable with those achieved in heterotrophic organisms. Efficient genetic engineering tools and metabolic modeling can accelerate the development of solar fuel and chemical production in cyanobacteria.
This review addresses the most recent approaches to produce solar fuels and chemicals in engineered cyanobacteria with a focus on acetyl-CoA-dependent products.
April 2020: Mohammad Ziaur Rahman, Haining Tian, and Tomas Edvinsson published an article in Angewandte Chemie International Edition:
Revisiting the Limiting Factors for Overall Water‐Splitting on Organic Photocatalysts
Abstract: In pursuit of inexpensive and earth abundant photocatalysts for solar hydrogen production from water, conjugated polymers have shown potential to be a viable alternative to widely used inorganic counterparts. The photocatalytic performance of polymeric photocatalysts, however, is very poor in comparison to that of inorganic photocatalysts. Most of the organic photocatalysts are active in hydrogen production only when a sacrificial electron donor (SED) is added into the solution, and their high performances often rely on presence of noble metal co‐catalyst (e.g. Pt). For pursuing a carbon neutral and cost‐effective green hydrogen production, unassisted hydrogen production solely from water is one of the critical requirements to translate a mere bench‐top research interest into the real world applications. Although this is a generic problem for both inorganic and organic types of photocatalysts, organic photocatalysts are mostly investigated in the half‐reaction and have so far shown limited success in hydrogen production from overall water‐splitting. To make progress, this article exclusively discusses critical factors that are limiting the overall water‐splitting in organic photocatalysts. Additionally, we also have extended the discussion to stability issues and the accurate reporting of the hydrogen production, and issues to be resolved to reach 10% STH (solar‐to‐hydrogen) conversion efficiency.
April 2020: M. Ibrahim, T. Fransson, R. Chatterjee, Mun Hon Cheah, R. Hussein, L. Lassalle, K. D. Sutherlin, I. D. Young, F. D. Fuller, S. Gul, I.-S. Kim, P.S. Simon, Casper de Lichtenberg, Petko Chernev, I. Bogacz, C. C. Pham, A. M. Orville, N. Saichek, T. Northen, A.r Batyuk, S. Carbajo, R. Alonso-Mori, K. Tono, S. Owada, A. Bhowmick, R. Bolotovsky, D. Mendez, N. W. Moriarty, J. M. Holton, H. Dobbek, A. S. Brewster, P. D. Adams, N. K. Sauter, U. Bergmann, A. Zouni, Johannes Messinger, J. Kern, V. K. Yachandra, and J. Yano published an article in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the U.S.A.:
Abstract: In oxygenic photosynthesis, light-driven oxidation of water to molecular oxygen is carried out by the oxygen-evolving complex (OEC) in photosystem II (PS II). Recently, we reported the room-temperature structures of PS II in the four (semi)stable S-states, S1, S2, S3, and S0, showing that a water molecule is inserted during the S2 → S3 transition, as a new bridging O(H)-ligand between Mn1 and Ca. To understand the sequence of events leading to the formation of this last stable intermediate state before O2 formation, we recorded diffraction and Mn X-ray emission spectroscopy (XES) data at several time points during the S2 → S3 transition. At the electron acceptor site, changes due to the two-electron redox chemistry at the quinones, QA and QB, are observed. At the donor site, tyrosine YZ and His190 H-bonded to it move by 50 µs after the second flash, and Glu189 moves away from Ca. This is followed by Mn1 and Mn4 moving apart, and the insertion of OX(H) at the open coordination site of Mn1. This water, possibly a ligand of Ca, could be supplied via a “water wheel”-like arrangement of five waters next to the OEC that is connected by a large channel to the bulk solvent. XES spectra show that Mn oxidation (τ of ∼350 µs) during the S2 → S3 transition mirrors the appearance of OX electron density. This indicates that the oxidation state change and the insertion of water as a bridging atom between Mn1 and Ca are highly correlated..
March 2020: Brian D. McCarthy, Anna M. Beiler, Ben A. Johnson, Timofey Liseev, Ashleigh T. Castner, and Sascha Ott published an article in Coordination Chemistry Reviews:
Analysis of Electrocatalytic Metal-organic Frameworks
Abstract: The electrochemical analysis of molecular catalysts for the conversion of bulk feedstocks into energy-rich clean fuels has seen dramatic advances in the last decade. More recently, increased attention has focused on the characterization of metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) containing well-defined redox and catalytically active sites, with the overall goal to develop structurally stable materials that are industrially relevant for large-scale solar fuel syntheses. Successful electrochemical analysis of such materials draws heavily on well-established homogeneous techniques, yet the nature of solid materials presents additional challenges. In this tutorial-style review, we cover the basics of electrochemical analysis of electroactive MOFs, including considerations of bulk stability, methods of attaching MOFs to electrodes, interpreting fundamental electrochemical data, and finally electrocatalytic kinetic characterization. We conclude with a perspective of some of the prospects and challenges in the field of electrocatalytic MOFs.
February 2020: Ouissam El Bakouri, Joshua R. Smith, and Henrik Ottosson published an article in Journal of the American Chemical Society:
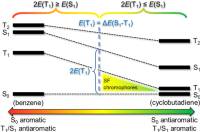
Singlet exciton fission photovoltaic technology requires chromophores with their lowest excited states arranged so that 2E(T1) < E(S1) and E(S1) < E(T2). Herein, qualitative theory and quantum chemical calculations are used to develop explicit strategies on how to use Baird’s 4n rule on excited-state aromaticity, combined with Hückel’s 4n + 2 rule for ground-state aromaticity, to tailor new potential chromophores for singlet fission. We first analyze the E(T1), E(S1), and E(T2) of benzene and cyclobutadiene (CBD) as excited-state antiaromatic and aromatic archetypes, respectively, and reveal that CBD fulfills the criteria on the state ordering for a singlet fission chromophore. We then look at fulvenes, a class of compounds that can be tuned by choice of substituents from Baird-antiaromatic to Baird-aromatic in T1 and S1 and from Hückel-aromatic to Hückel-antiaromatic in S0. The T1 and S1 states of most substituted fulvenes (159 of 225) are described by singly excited HOMO → LUMO configurations, providing a rational for the simultaneous tuning of E(T1) and E(S1) along an approximate (anti)aromaticity coordinate. Key to the tunability is the exchange integral (KH,L), which ideally is constant throughout the compound class, providing a constant ΔE(S1 – T1). This leads us to a geometric model for the identification of singlet fission chromophores, and we explore what factors limit the model. Candidates with calculated E(T1) values of ∼1 eV or higher are identified among benzannelated 4nπ-electron compound classes and siloles. In brief, it is clarified how the joint utilization of Baird’s 4n and Hückel’s 4n + 2 rules, together with substituent effects (electronic and steric) and benzannelation, can be used to tailor new chromophores with potential use in singlet fission photovoltaics.
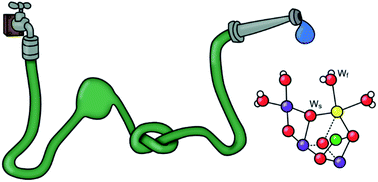
January 7, 2020: Mun Hon Cheah, Miao Zhang, Dmitry Shevela, Fikret Mamedov, Athina Zouni, and Johannes Messinger published an article in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the USA:
Significance: Photosynthetic water oxidation by the multi-subunit membrane protein complex PSII is an important process that sustains all aerobic life on Earth by producing molecular oxygen from sunlight and water. Understanding the mechanism of this process is crucial toward advancing fundamental knowledge as well as providing a blueprint for the development of solar fuel devices. Important pieces of information required for solving the mechanism of biological water oxidation are the oxidation states of the manganese ions forming the catalytic site of water oxidation in PSII. Here, we resolve a long-standing controversy between 2 competing schools of thought, by providing a clear-cut determination of overall manganese oxidation states using a simple counting experiment.
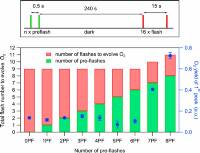
Fig. 4: (Top) Laser flash spacing’s used for photoactivation of apo-PSII microcrystals suspension by various combinations of tightly spaced preflashes (green line) and monitoring flashes (red line) with 15-s spacing. The dark time of 240 s was employed to allow the back reaction of the S2 and S3 states to S1. (Bottom) Total number of flashes required to observe the first O2 evolution (left axis) during the photoactivation of apo-PSII crystals with various combinations of preflashes and monitoring flashes (see Top). The yields of the first O2 peaks, plotted in blue, are the averages of 2 repeat measurements, and the error bars are SDs.
2019 publications
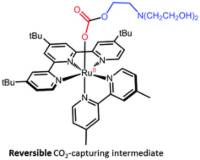
October 18 2019: Nicolas Queyriaux, Wesley B. Swords, Hemlata Agarwala, Ben A. Johnson, Sascha Ott and Leif Hammarström published an article in Dalton Transactions:
Abstract: The ability of [RuII(tButpy)(dmbpy)(MeCN)]2+ (1-MeCN) to capture CO2, with the assistance of triethanolamine (TEOA), has been assessed under photocatalytically-relevant conditions. The photolability of 1-MeCN has proven essential to generate a series of intermediates which only differ by the nature of their monodentate ligand. In DMF, ligand photoexchange of 1-MeCN to give [RuII(tButpy)(dmbpy)(DMF)]2+ (1-DMF) proceeds smoothly with a quantum yield of 0.011. However, in the presence of TEOA, this process was disrupted, leading to the formation of a mixture of 1-DMF and [RuII(tButpy)(dmbpy)(TEOA)]+ (1-TEOA). An equilibrium constant of 3 was determined. Interestingly, 1-TEOA demonstrated an ability to reversibly catch and release CO2 making it a potentially crucial intermediate towards CO2 reduction.
September 11 2019: Souvik Roy, Zhehao Huang, Asamanjoy Bhunia, Ashleigh Castner, Arvind K. Gupta, Xiaodong Zou, and Sascha Ott published an article in Journal of the American Chemical Society:
Electrocatalytic Hydrogen Evolution from a Cobaloxime-Based Metal–Organic Framework Thin Film.
Abstract: Molecular hydrogen evolution catalysts (HECs) are synthetically tunable and often exhibit high activity, but they are also hampered by stability concerns and practical limitations associated with their use in the homogeneous phase. Their incorporation as integral linker units in metal–organic frameworks (MOFs) can remedy these shortcomings. Moreover, the extended three-dimensional structure of MOFs gives rise to high catalyst loadings per geometric surface area. Herein, we report a new MOF that exclusively consists of cobaloximes, a widely studied HEC, that act as metallo-linkers between hexanuclear zirconium clusters. When grown on conducting substrates and under applied reductive potential, the cobaloxime linkers promote electron transport through the film as well as function as molecular HECs. The obtained turnover numbers are orders of magnitude higher than those of any other comparable cobaloxime system, and the molecular integrity of the cobaloxime catalysts is maintained for at least 18 h of electrocatalysis. Being one of the very few hydrogen evolving electrocatalytic MOFs based on a redox-active metallo-linker, this work explores uncharted terrain for greater catalyst diversity and charge transport pathways.
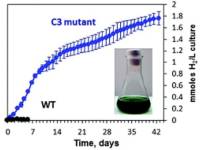
July 31 2019: Pilla Sankara Krishna, Stenbjörn Styring and Fikret Mamedov published an article in Green chemistry:
Photosystem ratio imbalance promotes direct sustainable H2 production in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii.
Abstract: The green alga Chlamydomonas reinhardtii can photoproduce H2 gas for only a few minutes under anaerobic conditions due to the inhibition of hydrogenase by O2 produced by Photosystem II (PSII). A few days of sustained H2 production can only be achieved when O2 and H2 production are temporally separated under two-stage processes such as sulfur deprivation. Under sulfur deprivation, H2 production is initiated after the over-reduction of the plastoquinone pool and decreased PSII activity in the thylakoid membrane. As a result, activated hydrogenase consumes the excess of electrons produced by PSII [Volgusheva et al., Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A., 2013, 110, 7223]. Here, we report that similar conditions can be achieved by simply altering the ratio between photosystem I (PSI) and PSII. In the C3 mutant of C. reinhardtii, we found a lower PSI/PSII ratio than in the wild type, 0.33 vs. 0.85, respectively. This imbalance of photosystems resulted in the over-reduced state of the plastoquinone pool and activation of hydrogenase in the C3 mutant that allowed the photoproduction of H2 continuously for 42 days. This is an unprecedented duration of H2 production in green algae under standard growth conditions without any nutrient limitation. Photosynthetic electron flow from PSII to hydrogenase was closely regulated during this long-term H2 production. The amount of PSII was decreased and the amount of PSI was increased reaching a PSI/PSII ratio of more than 5 as shown by EPR and fluorescence spectroscopy. This fine-tuning of photosystems allows to sustain the long-term production of H2 in C. reinhardtii by a direct photosynthetic pathway.
July 16 2019: Xufeng Liu, Rui Miao, Pia Lindberg and Peter Lindblad published an article in Energy & Environmental Science:
Modular Engineering for Efficient Photosynthetic Biosynthesis of 1-Butanol from CO2 in Cyanobacteria
Abstract: Cyanobacteria are photoautotrophic microorganisms which can be engineered to directly convert CO2 and water into biofuels and chemicals via photosynthesis using sunlight as energy. However, product titers and rates are main challenges that need to be overcome for industrial applications. Here we present a systematic modular engineering of the cyanobacterium Synechocystis PCC 6803, enabling efficient biosynthesis of 1-butanol, an attractive commodity chemical and gasoline substitute. Through introducing and re-casting the 1-butanol biosynthetic pathway at gene and enzyme levels, optimizing the 5’-regions of expression units for tuning transcription and translation, rewiring carbon flux and rewriting the photosynthetic central carbon metabolism to enhance the precursor supply, and performing process development, we were able to reach a cumulative 1-butanol titer of 4.8 g∙L-1 with a maximal rate of 302 mg∙L-1∙day-1 from the engineered Synechocystis. This represents the highest 1-butanol production from CO2 reported so far. Our multi-level modular strategy for high-level production of chemicals and advanced biofuels represents a blue-print for future systematic engineering in photosynthetic microorganisms.
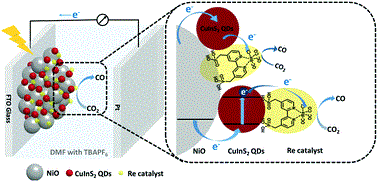
June 11 2019: Jing Huang, Bo Xu, Lei Tian, Palas Baran Pati, Ahmed S. Etman, Junliang Sun, Leif Hammarström and Haining Tian published an article in Chemical Communications:
Abstract: Heavy metal-free CuInS2 quantum dots (QDs) were employed as a photosensitizer on a NiO photocathode to drive an immobilized molecular Re catalyst for photoelectrochemical CO2 reduction for the first time. A photocurrent of 25 μA cm−2 at −0.87 V vs. NHE was obtained, providing a faradaic efficiency of 32% for CO production.
May 17 2019: Yaxiao Guo, Zhaoyang Yao, Brian J. Timmer, Xia Sheng, Lizhou Fan, YuanYuan Li, Fuguo Zhang, and Licheng Sun, published an article in Nano Energy:
Abstract: A facile preparation of bio-inspired and morphology controllable catalytic electrode FeS@MoS2/CFC, featuring a carbon fiber cloth (CFC) covered with FeS dotted MoS2 nanosheets, has been established. Synergy between the CFC as a self-standing conductive substrate and the FeS nanoparticle dotted MoS2 nanosheets with abundant active sites makes the noble-metal-free catalytic electrode FeS@MoS2/CFC highly efficient in nitrogen reduction reaction (NRR), with an ammonia production rate of 8.45 μg h−1 cm−2 and excellent long-term stability at −0.5 V in pH neutral electrolyte. Further electrolysis in acidic and alkaline electrolytes revealed the overall NRR catalytic activity of this electrode over a wide pH range.
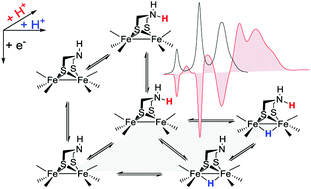
May 2 2019: Alexander Aster, Shihuai Wang, Mohammad Mirmohades, Charlène Esmieu, Gustav Berggren, Leif Hammarström and Reiner Lomoth published an article in Chemical Science:
Abstract: Electron and proton transfer reactions of diiron complexes [Fe2adt(CO)6] (1) and [Fe2adt(CO)4(PMe3)2] (4), with the biomimetic azadithiolate (adt) bridging ligand, have been investigated by real-time IR- and UV-vis-spectroscopic observation to elucidate the role of the adt-N as a potential proton shuttle in catalytic H2 formation. Protonation of the one-electron reduced complex, 1−, occurs on the adt-N yielding 1H and the same species is obtained by one-electron reduction of 1H+. The preference for ligand vs. metal protonation in the Fe2(I,0) state is presumably kinetic but no evidence for tautomerization of 1H to the hydride 1Hy was observed. This shows that the adt ligand does not work as a proton relay in the formation of hydride intermediates in the reduced catalyst. A hydride intermediate 1HHy+ is formed only by protonation of 1H with stronger acid. Adt protonation results in reduction of the catalyst at much less negative potential, but subsequent protonation of the metal centers is not slowed down, as would be expected according to the decrease in basicity. Thus, the adtH+ complex retains a high turnover frequency at the lowered overpotential. Instead of proton shuttling, we propose that this gain in catalytic performance compared to the propyldithiolate analogue might be rationalized in terms of lower reorganization energy for hydride formation with bulk acid upon adt protonation.
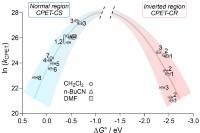
April 11 2019: Giovanny A. Parada, Zachary K. Goldsmith, Scott Kolmar, Belinda Pettersson Rimgard, Brandon Q. Mercado, Leif Hammarström, Sharon Hammes-Schiffer, and James M. Mayer published an article in Science:
Concerted proton-electron transfer reactions in the Marcus inverted region.
Abstract: Electron transfer (ET) reactions slow down when they become thermodynamically very favorable, a counterintuitive interplay of kinetics and thermodynamics termed the inverted region in Marcus theory. Here we report inverted region behavior for proton-coupled electron transfer (PCET). Specifically, photochemical studies of anthracene-phenol-pyridine triads give rate constants for PCET charge recombination that are slower for the more thermodynamically favorable reactions. Photoexcitation forms an anthracene excited state that undergoes PCET to create a charge separated state. The rate constants for return charge recombination show an inverted dependence on the driving force upon changing pyridine substituents and the solvent. Calculations using vibronically nonadiabatic PCET theory yield rate constants for simultaneous tunneling of the electron and proton that account for the results.
February 21 2019: Sonja Pullen, Somnath Maji, Matthias Stein and Sascha Ott published an article in Dalton transactions:
Abstract: A new series of homodinuclear iron complexes as models of the [FeFe]-hydrogenase active site was prepared and characterized. The complexes of the general formula [Fe2(mcbdt)(CO)5PPh2R] (mcbdt = benzene-1,2-dithiol-3-carboxylic acid) feature covalent tethers that link the mcbdt ligand with the phosphine ligands which are terminally coordinated to one of the Fe centres. The synthetic feasability of the concept is demonstrated with the preparation of three novel complexes. A detailed theoretical investigation showes that by introducing a rigid covalent link between the phosphine and the bridging dithiolate ligands, the rotation of the Fe(CO)2P unit is hindered and higher rotation barriers were calculated compared to nonlinked reference complexes. The concept of restricting Fe(L)3 rotation is an approach to kinetically stabilize terminal hydrides which are reactive intermediates in catalytic proton reduction cycles of the enzymes.
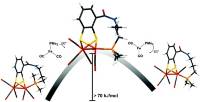
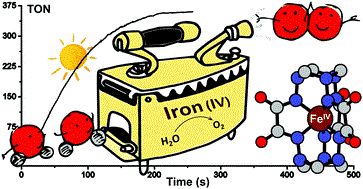
February 18 2019: Sergii I. Shylin, Mariia V. Pavliuk, Luca D’Amario, Fikret Mamedov, Jacinto Sá, Gustav Berggren and Igor O. Fritsky published an article in Chemical communications:
Efficient visible light-driven water oxidation catalysed by an iron(IV) clathrochelate complex.
Abstract: A water-stable Fe(IV) clathrochelate complex catalyses fast and homogeneous photochemical oxidation of water to dioxygen with a turnover frequency of 2.27 /s and a maximum turnover number of 365. An Fe(V) intermediate generated under catalytic conditions is trapped and characterised using EPR and Mössbauer spectroscopy.
January 4 2019: Kamonchanock Eungrasamee, Rui Miao, Aran Incharoensakdi, Peter Lindblad and Saowarath Jantaro published an article in Biotechnology for biofuels:
Abstract: Cyanobacteria are potential sources for third generation biofuels. Their capacity for biofuel production has been widely improved using metabolically engineered strains. In this study, we employed metabolic engineering design with target genes involved in selected processes including the fatty acid synthesis (a cassette of accD, accA, accC and accB encoding acetyl-CoA carboxylase, ACC), phospholipid hydrolysis (lipA encoding lipase A), alkane synthesis (aar encoding acyl-ACP reductase, AAR), and recycling of free fatty acid (FFA) (aas encoding acyl–acyl carrier protein synthetase, AAS) in the unicellular cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803.
January 3 2019: Brigitta Németh, Charlène Esmieu, Holly J. Redman and Gustav Berggren published an article in Dalton transactions:
Monitoring H-cluster assembly using a semisynthetic HydF protein.
Abstract: The [FeFe] hydrogenase enzyme interconverts protons and molecular hydrogen with remarkable efficiency. The reaction is catalysed by a unique metallo-cofactor denoted as the H-cluster containing an organometallic dinuclear Fe component, the [2Fe] subsite. The HydF protein delivers a precursor of the [2Fe] subsite to the apo-[FeFe] hydrogenase, thus completing the H-cluster and activating the enzyme. Herein we generate a semi-synthetic form of HydF by loading it with a synthetic low valent dinuclear Fe complex. We show that this semi-synthetic protein is practically indistinguishable from the native protein, and utilize this form of HydF to explore the mechanism of H-cluster assembly. More specifically, we show that transfer of the precatalyst from HydF to the hydrogenase enzyme results in the release of CO, underscoring that the pre-catalyst is a four CO species when bound to HydF. Moreover, we propose that an electron transfer reaction occurs during H-cluster assembly, resulting in an oxidation of the [2Fe] subsite with concomitant reduction of the [4Fe4S] cluster present on the HydF protein.
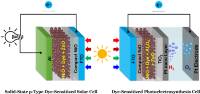
January 2019: Bo Xu, Lei Tian, Ahmed S.Etman, Junliang Sun, and Haining Tian published an article in Nano energy:
Abstract: A solution-processed NiO-dye-ZnO photocathode was developed for applications in both solid-state p-type dye-sensitized solar cells (p-ssDSCs) and p-type dye-sensitized photoelectrosynthesis cells (p-DSPECs). In p-ssDSCs, the solar cell using ZnO as electron transport material showed a short circuit current, up to 680 µA cm−2, which is 60-fold larger than that previously reported device using TiO2 as electron transport material with similar architecture. In the p-DSPECs, a remarkable photocurrent of 100 μA cm−2 was achieved in a pH = 5.0 acetate buffer solution under a bias potential at 0.05 V vs RHE with platinum as the proton reduction catalyst. A Faradaic efficiency approaching 100% for the H2 evolution reaction was obtained after photoelectrolysis for 9 h. Importantly, the solution-processed NiO-dye-ZnO photocathode exhibited excellent long-term stability in both p-ssDSCs and p-DSPECs. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first study where a solution-processable, nanoporous NiO-dye-ZnO photocathode is used for both p-ssDSCs and p-DSPECs having both excellent device performance and stability.
CAP 2022